1と13のリビジョン間の差分 (その間の編集: 12回)
|
サイズ: 34069
コメント:
|
サイズ: 29822
コメント:
|
| 削除された箇所はこのように表示されます。 | 追加された箇所はこのように表示されます。 |
| 行 3: | 行 3: |
| This section explains the usage methods common among [[ClusterSystem|the Next Generation Simulation Technology Education]] and [[WideAreaClusterSystem|the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research]]. See the page for each system for details of specific functions. | This section explains the usage methods common among [[ClusterSystem|the Next Generation Simulation Technology Education]] and [[en/WideAreaClusterSystem|the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research]]. See the page for each system for details of specific functions. |
| 行 7: | 行 7: |
| == ログイン方法 == /* * [[ClusterSystem|次世代シミュレーション技術教育計算機システム]]*/ * [[WideAreaClusterSystem|広域連携教育研究用クラスタシステム]] == 開発環境の設定方法 == 計算プログラムをコンパイルする場合,並列計算用 MPI やコンパイラに応じて環境変数を設定する必要があります. 例えば,並列計算用 MPI として Intel MPI を,コンパイラとして Intel コンパイラを利用したい場合は,以下のようにコマンドを実行して環境変数を設定して下さい.なお,ログイン直後はIntel MPIとIntel コンパイラが設定されています. |
== Logging In == /* * [[en/ClusterSystem|Computer Systems for the Next Generation Simulation Technology Education]]*/ * [[en/WideAreaClusterSystem|Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research]] == Setting Up the Developmental Environment == To compile a program, it is necessary to set environment variables depending on the parallel processing MPI and the compiler. For example, if you plan to use an Intel MPI as the parallel computing MPI and an Intel compiler as the compiler, set the environment variables using the following commands shown below. Note that the Intel MPI and the Intel compiler are set as the session defaults. |
| 行 17: | 行 17: |
| その他,以下の環境設定用コマンドが利用できます. ||並列計算用MPI ||コンパイラ ||設定用コマンド || ||Intel MPI ||Intel コンパイラ ||module load intelmpi.intel || ||Open MPI ||Intel コンパイラ ||module load openmpi.intel || ||MPICH2 ||Intel コンパイラ ||module load mpich2.intel || ||MPICH1 ||Intel コンパイラ ||module load mpich.intel || ||- ||Intel コンパイラ ||module load intel || ||- ||PGI コンパイラ ||module load pgi || ||- ||gcc コンパイラ ||module load gcc || ||- ||nvcc コンパイラ ||module load cuda-5.0 || 開発環境を切り替える際には,以下のコマンドを実行し既存の環境設定を削除した後,新しい開発環境を設定します. {{{ $ module unload 環境設定 }}} 例えば,IntelMPI, Intelコンパイラの環境から,OpenMPI,Intelコンパイラの環境へ変更する場合は,以下のようにしてください. |
You can also use the following commands to set the environment variables. ||Parallel computing MPI ||Compiler ||Environment variable setting command || ||Intel MPI ||Intel compiler ||module load intelmpi.intel || ||Open MPI ||Intel compiler ||module load openmpi.intel || ||MPICH2 ||Intel compiler ||module load mpich2.intel || ||MPICH1 ||Intel compiler ||module load mpich.intel || ||- ||Intel compiler ||module load intel || ||- ||PGI compiler ||module load pgi || ||- ||gcc compiler ||module load gcc || ||- ||nnvcc compiler ||module load cuda-5.0 || To change the environmental settings, execute the following command to delete the current settings and set the new environment variables. {{{ $ module unload environmental_settings }}} For example, if you change the Intel MPI and the Intel compiler to the Open MPI and the Intel compiler, execute as follows. |
| 行 42: | 行 39: |
| == ソフトウェア利用環境の設定方法 == 各種ソフトウエアを利用する場合,利用するソフトウエアに応じて環境変数を設定する必要があります. 例えば,Gaussianを利用したい場合は,以下のようにコマンドを実行して環境変数を設定して下さい. |
== Setting Up the Software Usage Environment == When using software, it is necessary to change the environment variables depending on the software package to be used. For example, use the following command to set the environment variables to use Gaussian. |
| 行 48: | 行 45: |
| その他,以下の環境設定用コマンドが利用できます. ||ソフトウエア名 ||バージョン ||設定用コマンド || ||||||<style="text-align:center">構造解析 || |
You can also use the following commands to set the environment variables. ||Software name ||Version ||Environment variable setting command || ||||||<style="text-align:center">Structural analysis || |
| 行 55: | 行 52: |
| ||||||<style="text-align:center">計算物質科学 || ||PHASE (Serial版) ||11.00 ||module load phase-11.00-serial || ||PHASE (Parallel版) ||11.00 ||module load phase-11.00-parallel || |
||||||<style="text-align:center">Computational materials science || ||PHASE (Serial version) ||11.00 ||module load phase-11.00-serial || ||PHASE (Parallel version) ||11.00 ||module load phase-11.00-parallel || |
| 行 59: | 行 56: |
| ||UVSOR (Serial版) ||3.42 ||module load uvsor-v342-serial || ||UVSOR (Parallel版) ||3.42 ||module load uvsor-v342-parallel || ||OpenMX (Serial版) ||3.6 ||module load openmx-3.6-serial || ||OpenMX (Parallel版) ||3.6 ||module load openmx-3.6-parallel || ||||||<style="text-align:center">計算化学 || |
||UVSOR (Serial version) ||3.42 ||module load uvsor-v342-serial || ||UVSOR (Parallel version) ||3.42 ||module load uvsor-v342-parallel || ||OpenMX (Serial version) ||3.6 ||module load openmx-3.6-serial || ||OpenMX (Parallel version) ||3.6 ||module load openmx-3.6-parallel || ||||||<style="text-align:center">Computational Science || |
| 行 65: | 行 62: |
| ||NWChem (Serial版) ||6.1.1 ||module load nwchem-6.1.1-serial || ||NWChem (Parallel版) ||6.1.1 ||module load nwchem-6.1.1-parallel || ||GAMESS (Serial版) ||2012.R2 ||module load gamess-2012.r2-serial || ||GAMESS (Parallel版) ||2012.R2 ||module load gamess-2012.r2-parallel || |
||NWChem (Serial version) ||6.1.1 ||module load nwchem-6.1.1-serial || ||NWChem (Parallel version) ||6.1.1 ||module load nwchem-6.1.1-parallel || ||GAMESS (Serial version) ||2012.R2 ||module load gamess-2012.r2-serial || ||GAMESS (Parallel version) ||2012.R2 ||module load gamess-2012.r2-parallel || |
| 行 70: | 行 67: |
| ||Amber, AmberTools (Serial版) ||12 ||module load amber12-serial || ||Amber, AmberTools (Parallel版) ||12 ||module load amber12-parallel || ||CONFLEX (Serial版,Parallel版) ||7 ||module load conflex7 || ||||||<style="text-align:center">技術処理 || |
||Amber, AmberTools (Serial version) ||12 ||module load amber12-serial || ||Amber, AmberTools (Parallel version) ||12 ||module load amber12-parallel || ||CONFLEX (Serial version & Parallel version) ||7 ||module load conflex7 || ||||||<style="text-align:center">Technical processing || |
| 行 76: | 行 73: |
* ANSYS, ABAQUS, Patran, DEFORM-3D, GAUSSIAN, CHEMKIN-PRO, MATLABの利用には登録種別Aへの利用登録が必要です. * 登録種別Aの申請方法は http://imc.tut.ac.jp/research/form を参照してください. ソフトウエアの環境設定を削除する場合は,以下のコマンドを実行してください. {{{ $ module unload 環境設定 }}} 例えば,Gaussianの環境設定を削除する場合は以下のようにしてください. |
* You must be a Type A user to use ANSYS, ABAQUS, Patran, DEFORM-3D, GAUSSIAN, CHEMKIN-PRO, and MATLAB. * To apply for registration as a Type A user, see: http://imc.tut.ac.jp/en/research/form. To cancel the software environment, execute the following command. {{{ $ module unload environmental_settings }}} For example, to discard the Gaussian environmental setting, use the following command. |
| 行 92: | 行 87: |
| == ログイン後の環境設定方法 == 以下のファイルを編集することで,ログイン後の環境を自動的に設定することができます. * shの場合: ~/.profile * bashの場合: ~/.bash_profile * cshの場合: ~/.cshrc 例1: bash を利用していて,ログイン後の環境設定として,ansys, gaussian, conflexを利用できるようにする場合,以下を ~/.bashrc に追加. |
== Setting Up the Session Environment == Editing the following files automatically sets up the session environment after logging in. * When using sh: ~/.profile * When using bash: ~/.bash_profile * When using csh: ~/.cshrc Example 1: To use ansys, gaussian, and conflex in your session through bash, add the following codes to ~/.bashrc. |
| 行 106: | 行 101: |
| 例2: csh を利用していて,ログイン後の環境設定として,OpenMPI, Intel Compiler, gaussian, conflexを利用できるようにする場合,以下を ~/.cshrc に追加. | Example 2: To use OpenMPI, Intel Compiler, gaussian, and conflex in your session through csh, add the following codes to ~/.cshrc. |
| 行 114: | 行 109: |
| ロードしているモジュールは以下のコマンドにより確認できます. | The following command displays the currently loaded modules. |
| 行 119: | 行 114: |
| 利用できるモジュールは以下のコマンドにより確認できます. | The following command displays the available modules. |
| 行 124: | 行 119: |
| == コンパイル方法 == === Intel コンパイラ === C/C++ で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ icc ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} Fortran で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ ifort ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} === PGI コンパイラ === C/C++ で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ pgcc ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} Fortran で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ pgf90 ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} {{{ $ pgf77 ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} === GNU コンパイラ === C/C++ で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ gcc ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 |
== Compiling == === Intel Compiler === To compile a C/C++ program, execute the following command. {{{ $ icc source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} To compile a FORTRAN program, execute the following command. {{{ $ ifort source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} === PGI Compiler === To compile a C/C++ program, execute the following command. {{{ $ pgcc source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} To compile a FORTRAN program, execute the following command. {{{ $ pgf90 source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} {{{ $ pgf77 source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} === GNU Compiler === To compile a C/C++ program, execute the following command. {{{ $ gcc source_file_name –o output_program_name |
| 行 157: | 行 152: |
| C/C++ で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ mpiicc ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} Fortran で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ mpiifortソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 |
To compile a C/C++ program, execute the following command. {{{ $ mpiicc source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} To compile a FORTRAN program, execute the following command. {{{ $ mpiifort source_file_name –o output_program_name |
| 行 168: | 行 163: |
| C/C++ で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ mpicc ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} Fortran で記述された計算プログラムをコンパイルするには,以下のコマンドを実行して下さい. {{{ $ mpif90 ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} {{{ $ mpif77 ソースファイル名 -o 出力するプログラム名 }}} == ジョブ実行方法 == ジョブの管理のため,ジョブ管理システムTorqueを使用しています. 必ず,Torqueを利用してジョブを実行してください. === キュー構成 === /* * [[ClusterSystem|次世代シミュレーション技術教育計算機システム]] */ * [[WideAreaClusterSystem|広域連携教育研究用クラスタシステム]] === ジョブ投入方法 === Torque用の実行スクリプトを作成し,qsubコマンドで次のようにジョブを投入します. {{{ $ qsub -q キュー名 実行スクリプト名 }}} 例えば,研究用キューrchqにジョブを投入する場合は次のようにします. {{{ $ qsub -q rchq 実行スクリプト名 }}} 並列数の指定は,実行スクリプト中で次のように行います. {{{ #PBS -l nodes=使用ノード数:ppn=1ノードあたりの並列数 }}} 例:1ノードを利用し,ノード内の並列数を16とした場合 |
To compile a C/C++ program, execute the following command. {{{ $ mpicc source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} To compile a FORTRAN program, execute the following command. {{{ $ mpif90 source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} {{{ $ mpif77 source_file_name –o output_program_name }}} == Executing Jobs == The job management system, Torque, is used to manage jobs to be executed. Always use Torque to execute jobs. === Queue Configuration === * [[en/WideAreaClusterSystem|Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research]] === Submitting Jobs === Create the Torque script and submit the job as follows using the qsub command. {{{ $ qsub –q quque_name script_name }}} For example, enter the following to submit a job to rchq, a research job queue. {{{ $ qsub -q rchq script_name }}} In the script, specify the number of processors per node to request as follows. {{{ #PBS -l nodes=no_of_nodes:ppn=processors_per_node }}} Example: To request 1 node and 16 processors per node |
| 行 209: | 行 202: |
| 例:4ノードを利用し,各ノード内の並列数を16とした場合 | Example: To request 4 nodes and 16 processors per node |
| 行 214: | 行 207: |
| 利用するメモリ容量を指定して実行したい場合は,実行スクリプト中で次のように記述します. {{{ #PBS -l nodes=使用ノード数:ppn=1ノードあたりの並列数,mem=ジョブあたりのメモリ容量 }}} 例:1ノードを利用し,ノード内の並列数を16,ジョブあたりのメモリ容量を16GBとした場合 |
To execute a job with the specified memory capacity, add the following codes to the script. {{{ #PBS -l nodes=no_of_nodes:ppn=processors_per_node,mem=memory_per_job }}} Example: To request 1 node, 16 processors per node, and 16GB memory per job |
| 行 224: | 行 217: |
| 利用する演算ノードを指定して実行したい場合は,次のように記述します. {{{ #PBS -l nodes=ホストA:ppn=ホストAでの並列数+ホストB:ppn=ホストBでの並列数,・・・ }}} 例:演算ノードcsnd00,csnd01を利用し,各ノード内の並列数を16とした場合 |
To execute a job with the specified calculation node, add the following codes to the script. {{{ #PBS -l nodes=nodeA:ppn=processors_for_nodeA+nodeB:ppn= processors_for_nodeB,・・・ }}} Example: To request csnd00 and csnd01 as the nodes and 16 processors per node |
| 行 234: | 行 226: |
| * 演算ノードのホスト名はcsnd00~csnd27です(システム構成-ハードウェア構成 参照). * csnd00,csnd01はTesla K20Xを搭載しています. GPGPU搭載の演算ノードを指定して実行したい場合は,次のように記述します. |
* From csnd00 to csnd27 are the calculation nodes (see Hardware Configuration under System Configuration). * csnd00 and csnd01 are equipped with Tesla K20X. To execute a job on a calculation node with GPGPU, add the following codes to the script. |
| 行 243: | 行 235: |
| ジョブ実行時間を指定して実行したい場合は,次のように記述します. | To execute a job in a specified duration of time, add the following codes to the script. |
| 行 248: | 行 240: |
| 例:ジョブ実行時間を336時間とする場合 | Example: To request a duration of 336 hours to execute a job |
| 行 253: | 行 245: |
| qsubコマンドの主なオプションを以下に示します. ||オプション ||使用例 ||意味 || ||-e ||-e filename ||標準エラー出力の内容を指定されたファイル名に出力する.-eオプションが指定されていない場合は,qsubコマンドが実行されたディレクトリ上に作成される.その際のファイル名は“ジョブ名.eジョブ番号”になる. || ||-o ||-o filename ||標準出力の内容を指定されたファイル名に出力する.-oオプションが指定されていない場合は,qsubコマンドが実行されたディレクトリ上に作成される.その際のファイル名は“ジョブ名.oジョブ番号”になる. || ||-j ||-j join ||標準出力,標準エラー出力を1個のファイルにマージするかしないかの動作を指定する.<<BR>>-j oe:標準出力に標準エラー出力をマージする<<BR>>-j eo:標準エラー出力に標準出力をマージする<<BR>>-j n: 標準出力と標準エラー出力をマージしない(デフォルト) || ||-q ||-q destination ||ジョブを投入するキューを指定する. || ||-l ||-l resource_list ||ジョブの実行に必要なリソース資源を指定する. || ||-N ||-N name ||ジョブ名を指定する(文字数は15文字まで).デフォルトはスクリプトでジョブが投入された場合は,スクリプトのファイル名となる.そうでない場合は,“STDIN”になる. || ||-m ||-m mail_events ||ジョブの状態をメールで通知する指定を行う.<<BR>>-m n:メールを送信しない<<BR>>-m a:異常終了時<<BR>>-m b:処理開始時<<BR>>-m e:処理終了時 || ||-M ||-M user_list ||メールを送信するメールアドレスを指定する. || ==== サンプルスクリプト:Intel MPI - Intelコンパイラを使用する場合 ==== |
The major options of the '''qsub''' command are as follows. ||Option ||Example ||Description || ||-e ||-e filename ||Outputs the standard error to a specified file. When the '''-e''' option is not used, the output file is created in the directory where the '''qsub''' command was executed. The file name convention is job_name.ejob_no. || ||-o ||-o filename ||Outputs the standard output to the specified file. When the '''-o''' option is not used, the output file is created in the directory where the '''qsub''' command was executed. The file name convention is job_name.ojob_no. || ||-j ||-j join ||Specifies whether to merge the standard output and the standard error to a single file or not.<<BR>>-j oe: Merges the standard error into the standard output file.<<BR>>-j eo: Merges the standard output into the standard error file.<<BR>>-j n: Does not merge the standard error file and the standard output file (Default). || ||-q ||-q destination ||Specifies the queue to submit a job. || ||-l ||-l resource_list ||Specifies the resources required for job execution. || ||-N ||-N name ||Specifies the job name (up to 15 characters). If a job is submitted via a script, the script file name is used as the job name by default. Otherwise, '''STDIN''' is used. || ||-m ||-m mail_events ||Notifies the job status by an email.<<BR>>-m n: Does not send an email.<<BR>>-m a: Sends an email if the job terminates abnormally.<<BR>>-m b: Sends an email when the job execution starts.<<BR>>-m e: Sends an email when the job execution ends. || ||-M ||-M user_list ||Specifies the email address to receive the notice. || ==== Sample Script: When Using an Intel MPI and an Intel Compiler ==== |
| 行 281: | 行 273: |
| * ジョブの投入先(eduq, rchq)はスクリプト内でも指定できます. ==== サンプルスクリプト:OpenMPI - Intelコンパイラを使用する場合 ==== |
* The target queue (either eduq or rchq) to submit the job can be specified in the script. ==== Sample Script: When Using an OpenMPI and an Intel Compiler ==== |
| 行 302: | 行 294: |
| * ジョブの投入先(eduq, rchq)はスクリプト内でも指定できます. ==== サンプルスクリプト:MPICH2 - Intelコンパイラを使用する場合 ==== |
* The target queue (either eduq or rchq) to submit the job can be specified in the script. ==== Sample Script: When Using an MPICH2 and an Intel Compiler ==== |
| 行 323: | 行 315: |
| * MPICH2を使用する場合は,必ず,-ifaceオプションを指定してください. * ジョブの投入先(eduq, rchq)はスクリプト内でも指定できます. ==== サンプルスクリプト:OpenMPプログラムを利用する場合 ==== |
* When using MPICH2, always specify the '''-iface''' option. * The target queue (either eduq or rchq) to submit the job can be specified in the script. ==== Sample Script: When Using an OpenMP Program ==== |
| 行 344: | 行 336: |
| ==== サンプルスクリプト:MPI/OpenMPハイブリドプログラムを利用する場合 ==== | ==== Sample Script: When Using an MPI/OpenMP Hybrid Program ==== |
| 行 363: | 行 355: |
| ==== サンプルスクリプト:GPGPUプログラムを利用する場合 ==== | ==== Sample Script: When Using a GPGPU Program ==== |
| 行 380: | 行 372: |
| === ANSYS Multiphysicsジョブ === ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
=== ANSYS Multiphysics Job === ==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 399: | 行 391: |
| *vm1.datは/common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/ansys/data/verifにあります. ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. 例:Shared Memory ANSYSを用いる場合 |
* vm1.dat exists in /common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/ansys/data/verif. ==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. Example: When using Shared Memory ANSYS |
| 行 421: | 行 413: |
| 例:Distributed ANSYSを用いる場合 |
Example: When using Distributed ANSYS |
| 行 438: | 行 429: |
| *vm141.datは/common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/ansys/data/verifにあります. === ANSYS CFXジョブ === ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
* vm141.dat exists in /common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/ansys/data/verif === ANSYS CFX Job === ==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 459: | 行 449: |
| *StaticMixer.defは/common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/CFX/examplesにあります. ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
* Static''''''Mixer.def exists in /common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/CFX/examples. ==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 479: | 行 469: |
| *StaticMixer.defは/common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/CFX/examplesにあります. === ANSYS Fluentジョブ === ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
*Static''''''Mixer.def exits in /common/ansys14.5/ansys_inc/v145/CFX/examples. === ANSYS Fluent Job === ==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 500: | 行 490: |
| ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 518: | 行 507: |
| === ANSYS LS-DYNAジョブ === ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
=== ANSYS LS-DYNA Job === ==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 537: | 行 526: |
| *hourglass.kはLS-DYNA Examples(http://www.dynaexamples.com/)を参照してください. === ABAQUSジョブ === ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
* For hourglass.k, see LS-DYNA Examples (http://www.dynaexamples.com/). === ABAQUS Job === ==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 558: | 行 547: |
| *1_mass_coarse.inpは/common/abaqus-6.12-3/6.12-3/samples/job_archive/samples.zipにあります. === PHASEジョブ === ==== 並列ジョブ (phaseコマンド:SCF計算) ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
*1_mass_coarse.inp exits in /common/abaqus-6.12-3/6.12-3/samples/job_archive/samples.zip. === PHASE Job === ==== Parallel Jobs (phase command: SCF calculation) ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 578: | 行 567: |
| * phaseの場合、入出力ファイル一式はfile_names.dataという名前のファイルで記述されます. * 入力ファイル一式として例えば、/common/phase-11.00-parallel/sample/Si2/scf/下のサンプルなどを利用できます. ==== シングルジョブ (ekcalコマンド:Band計算) ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
* For PHASE jobs, a set of I/O files are defined as file_names.data. * Sample input files are available at /common/phase-11.00-parallel/sample/Si2/scf/. ==== Single Job (ekcal command: Band calculation) ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 599: | 行 588: |
| * ekcalの場合、入出力ファイル一式はfile_names.dataという名前のファイルで記述されます. * 入力ファイル一式として例えば、/common/phase-11.00-parallel/sample/Si2/band/下のサンプルなどを利用できます. * (Si2/band/のサンプルを使用するには、予め../scf/のサンプルを実行してnfchgt.dataを用意しておく必要があります。). === UVSORジョブ === ==== 並列ジョブ (epsmainコマンド:誘電率計算) ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
* For ekcal jobs, a set of I/O files are defined as file_names.data. * Sample input files are available at /common/phase-11.00-parallel/sample/Si2/band/. * (Prior to using the sample files under Si2/band/, execute the sample file in ../scf/ to create nfchgt.data.) === UVSOR Job === ==== Parallel Jobs (epsmain command: Dielectric constant calculation) ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 623: | 行 611: |
| * epsmainの場合、入出力ファイル一式はfile_names.dataという名前のファイルで記述されます. * 入力ファイル一式として例えば、/common/uvsor-v342-parallel/sample/electron/Si/eps/下のサンプルなどを利用できます. * (Si/eps/のサンプルを使用するには、予め、../scf/のサンプルを実行してnfchgt.dataを用意しておく必要があります。). === OpenMXジョブ === ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
* For epsmain jobs, a set of I/O files are defined as file_names.data. * Sample input files are available at /common/uvsor-v342-parallel/sample/electron/Si/eps/. * (Prior to using the sample files under Si/eps/, execute the sample file in ../scf/ to create nfchgt.data.) === OpenMX Job === ==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 647: | 行 635: |
| * H2O.datは/common/openmx-3.6-parallel/work/にあります. * ただし、H2O.datに以下の一行を追加しておく必要があります. |
* H2O.dat exists in /common/openmx-3.6-parallel/work/. * The following line must be added to H2O.dat. |
| 行 653: | 行 641: |
| === GAUSSIANジョブ === サンプル入力ファイル(methane.com) |
=== GAUSSIAN Job === Sample input file (methane.com) e |
| 行 672: | 行 660: |
| ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 690: | 行 678: |
| ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 708: | 行 695: |
| === NWChemジョブ === サンプル入力ファイル(h2o.nw) |
=== NWChem Job === Sample input file (h2o.nw) |
| 行 732: | 行 719: |
| ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 750: | 行 736: |
| === GAMESSジョブ === ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
=== GAMESS Job === ==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 769: | 行 755: |
| * exam01.inpは/common/gamess-2012.r2-serial/tests/standard/にあります. === MPQCジョブ === サンプル入力ファイル(h2o.in) |
* exam01.inp exists in /common/gamess-2012.r2-serial/tests/standard/. === MPQC Job === Sample input file (h2o.in) |
| 行 784: | 行 769: |
| ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 803: | 行 788: |
| === AMBERジョブ === サンプル入力ファイル(gbin-sander) |
=== AMBER Job === Sample input file (gbin-sander) |
| 行 820: | 行 805: |
| サンプル入力ファイル(gbin-pmemd) | Sample input file (gbin-pmemd) |
| 行 837: | 行 822: |
| ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. 例:sanderを用いる場合 |
==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. Example: To use sander |
| 行 857: | 行 842: |
| *prmtop, eq1.xは/common/amber12-parallel/test/4096watにあります. 例:pmemdを用いる場合 |
* prmtop and eq1.x exists in /common/amber12-parallel/test/4096wat. Example: To use pmemd |
| 行 876: | 行 861: |
| *prmtop, eq1.xは/common/amber12-parallel/test/4096watにあります. ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. 例:sanderを用いる場合 |
* prmtop and eq1.x exists in /common/amber12-parallel/test/4096wat. ==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. Example: To use sander |
| 行 900: | 行 885: |
| *prmtop, eq1.xは/common/amber12-parallel/test/4096watにあります. 例:pmemd を用いる場合 |
* prmtop and eq1.x exists in /common/amber12-parallel/test/4096wat. Example: To use pmemd |
| 行 921: | 行 906: |
| *prmtop, eq1.xは/common/amber12-parallel/test/4096watにあります. === CONFLEXジョブ === サンプル入力ファイル(methane.mol) |
* prmtop and eq1.x exists in /common/amber12-parallel/test/4096wat. === CONFLEX Job === Sample input file (methane.mol) |
| 行 942: | 行 927: |
| ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 959: | 行 944: |
| ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 実行スクリプトを作成しqsubコマンドよりジョブを投入します. 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Parallel Jobs ==== Create the script and submit the job using the '''qsub''' command. The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 977: | 行 961: |
| === MATLABジョブ === サンプル入力ファイル(matlabdemo.m) |
=== MATLAB Job === Sample input file (matlabdemo.m) |
| 行 998: | 行 982: |
| ==== シングルジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Single Job ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 1016: | 行 1000: |
| ==== 並列ジョブ ==== 以下に,実行スクリプト例を示します. |
==== Parallel Jobs ==== The sample script is as follows. |
| 行 1034: | 行 1018: |
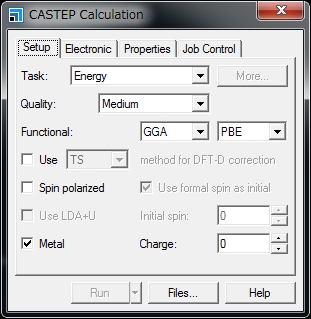
| === CASTEP/DMol3ジョブ === 本学スパコンを利用してMaterials Studio CASTEP/DMol3を実行する場合, ① Materials Studio Visualiserからスパコンに対しジョブを投入する(Materials Studio2016のみ対応) ② 入力ファイルをWinscp等でスパコンに転送し「qsub」コマンドによりジョブを投入する の二通りがあります.ここでは②について説明します.②で実行する場合,ジョブスケジューラに与えるパラメータを変更することができます.以下では,CASTEPを例に説明します. '''1. Materials Studio Visualizerで入力ファイルを作成します.''' 「CASTEP Calculation」ウィンドウの「Files...」をクリックします. |
=== CASTEP/DMol3 Job === There are two ways to run Materials Studio CASTEP/DMol3 using the University’s supercomputer: (1) Submit the job from Materials Studio Visualiser to the supercomputer (only Materials Studio 2016 is supported). (2) Transfer the input file to the supercomputer using Winscp etc. and submit the job using the '''qsub''' command. This section explains about the method (2). To submit the job in the method (2), the parameters to pass the job scheduler can be changed. The following is an example using CASTEP. '''1. Create an input file using Materials Studio Visualizer.''' In the '''CASTEP Calculation''' window, click '''Files…'''. |
| 行 1049: | 行 1033: |
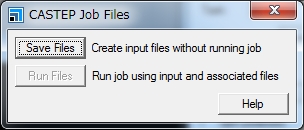
| 次に,「CASTEP Job Files」ウィンドウの「Save Files」をクリックします. | In the '''CASTEP Job Files''' window, click '''Save Files'''. |
| 行 1053: | 行 1037: |
| 入力ファイルは (任意のパス)\(プロジェクト名)_Files\Documents\(上記操作において作成されたフォルダ)\ に保存されます.例えば,acetanilide.xsdに対してCASTEPによりエネルギー計算を行う場合、「(上記操作において作成されたフォルダ)」は「acetanilide CASTEP Energy」となります. また,「(任意のパス)」は,通常,「C:\Users\(アカウント名)\Documents\Materials Studio Projects」です. 作成されるフォルダの名前にはスペースが含まれます.スペースを削除するか,”_”などで置換してください.また,フォルダ名に日本語が含まれてはいけません. '''2. Winscp等のファイル転送ソフトを利用し,作成した入力ファイルをフォルダごと本学スパコンへ転送してください.''' '''3. 転送したフォルダ内に下記のような実行スクリプトを作成し,「qsub」コマンドによりジョブを投入してください.''' |
The input file is stored at: specified_path\project_name_Files\Documents\folder_created_in_above_step For example, when performing an energy calculation using '''acetanilide.xsd''' in CASTEP following the above steps, the folder is created with the name of '''acetanilide CASTEP Energy'''. The above specified_path is usually C:\Users\account_name\Documents\Materials Studio Projects. The folder name contains a blank character. Delete the blank character or replace it with underscore (_). The folder name must not contain Japanese characters. '''2. Using file transfer software such as Winscp, transfer the created folder and the file it contains to the supercomputer. ''' '''3. Create a script as follows in the transferred folder and submit the job using the qsub command.''' |
| 行 1087: | 行 1072: |
| * RunCASTEP.shの第3引数は,転送したフォルダ内のファイル名を指定してください.拡張子は必要ありません. * 「ppn=」は,8以下,の値を指定してください. * 経過時間制限値,メモリ利用容量制限値は必要に応じて変更できます. * 「CASTEP Calculation」ウィンドウの”Job Control”タブにおける「Gateway location」「Queue」「Run in parallel on」の設定はコマンドライン実行に対し意味を持ちません.qsubコマンド時に利用する実行スクリプト内の設定が用いられます. * 実行スクリプトは利用する計算機や計算モジュールにより異なります.下記の「実行スクリプト例」をご参照ください. '''4. ジョブ終了後、計算結果ファイルをクライアントPCに転送し,Materials studio Visualizerを利用して閲覧してください.''' '''共同利用に関する注意事項''' Materials Studioのライセンスは,CASTEP:8本,Dmol3:8本,を所有しています.1ライセンスで8並列以下のジョブを1つ実行することができます.本ライセンスは共用です.他のユーザーと競合しないように留意の上,ご利用をお願いします. '''実行スクリプト例''' 広域連携教育研究用クラスタシステムでMaterials Studio 8.0 CASTEPを実行する場合: |
* Specify the file name without an extension in the transferred folder as the third argument in '''RunCASTEP.sh'''. * Specify a value of 8 or less in '''=ppn'''. * The values for the duration of job execution and the permitted memory capacity can be changed as necessary. * Specifications in the '''Gateway location, Queue''', and '''Run in parallel on''' fields in the '''Job Control''' tab in the '''CASTEP Calculation''' window will be ignored in job execution from the command line. The settings specified in the script used with the '''qsub''' command will be used. * The script contents vary depending on the computer and calculation modules to be used. See the following Example Scripts. '''4. After the job is completed, transfer the result file to your client PC and view the results using Materials studio Visualizer.''' '''Notes on Joint Research''' There are eight Materials Studio licenses owned by the University for CASTEP and a further eight for Dmol3. 1One job with eight or less parallel executions can be conducted under a single license. These licenses are shared. Avoid exclusively occupying the licenses and consider other users. '''Example Scripts''' Running Materials Studio 8.0 CASTEP in the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research |
| 行 1129: | 行 1114: |
| 広域連携教育研究用クラスタシステムでMaterials Studio 8.0 DMOL3を実行する場合: | Running Materials Studio 8.0 DMOL3 in the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research |
| 行 1151: | 行 1136: |
| 広域連携教育研究用クラスタシステムでMaterials Studio 2016 CASTEPを実行する場合: | Running Materials Studio 2016 CASTEP in the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research |
| 行 1174: | 行 1159: |
| 広域連携教育研究用クラスタシステムでMaterials Studio 2016 DMOL3を実行する場合: | Running Materials Studio 2016 DMOL3 in the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research |
| 行 1197: | 行 1182: |
| == ジョブの状態を確認する == ジョブ,キューの状態確認にはqstatコマンドを利用します. (1) ジョブの状態表示 |
== Viewing Job Status == Use the '''qstat''' command to view the job or queue status. (1) Viewing the job status |
| 行 1205: | 行 1190: |
| (2) キューの状態表示 | (2) Viewing the queue status |
| 行 1210: | 行 1195: |
| qstatコマンドの主なオプションを以下に示します. ||オプション ||使用例 ||意味 || ||-a ||-a ||すべてのキューイング・実行中のジョブを表示する. || ||-Q ||-Q ||すべてのキューの状態を簡易表示する. || ||-Qf ||-Qf ||すべてのキューの状態を詳細表示する. || ||-q ||-q ||キューの制限値を表示する. || ||-n ||-n ||ジョブに割り当てた計算ノードのホスト名を表示する. || ||-r ||-r ||実行中のジョブのリストを表示させます. || ||-i ||-i ||非実行中のジョブのリストを表示する. || ||-u ||-u ユーザ名 ||指定したユーザのジョブのリストを表示する. || ||-f ||-f ジョブID ||指定したジョブIDの詳細情報を表示する. || == 投入したジョブをキャンセルする == ジョブのキャンセルにはqdelコマンドを使用します. |
Major options for the '''qstat''' command are as follows. ||Options ||Usage ||Description || ||-a ||-a ||Displays all jobs in the queue and jobs being executed. || ||-Q ||-Q ||Displays the statuses of all queues in an abbreviated form. || ||-Qf ||-Qf ||Displays the statuses of all queues in a detailed form. || ||-q ||-q ||Displays the limitation values of the queues. || ||-n ||-n ||Displays the calculation node name assigned to the job. || ||-r ||-r ||Displays a list of running jobs. || ||-i ||-i ||Displays a list of idle jobs. || ||-u ||-u user_name ||Displays the jobs owned by the specified user. || ||-f ||-f job_ID ||Displays details of the job that has the specified job ID. || == Canceling a Submitted Job == Use the '''qdel''' command to cancel the submitted job. |
| 行 1231: | 行 1214: |
| job IDはqstatコマンドより確認してください. | Check the job ID beforehand using the '''qstat''' command. |
Using Cluster Systems
This section explains the usage methods common among the Next Generation Simulation Technology Education and the Wide-Area Coordinated Cluster System for Education and Research. See the page for each system for details of specific functions.
目次